The GY-NEO-7M Gps device is a GPS Navigation module that supports the Serial communication protocol and it has an active antenna. This module can be easily combined with any microcontroller. This module has a battery pack and can also be attached to a PC via a USB to TTL converter. This device can obtain data and then measure the geographic location with high precision and reliability. the module supports g BeiDou, Galileo, GLONASS, GPS / QZSS, and more the device has internal storage for saving configurations
AED 49.95
Description
The GY-NEO-7M GPS device is a GPS Navigation module that supports the Serial communication protocol and has an active antenna. This module can be easily combined with any microcontroller. This module has a battery pack and can be attached to a PC via a USB to TTL converter. This device can obtain data and measure the geographic location with high precision and reliability. the module supports g BeiDou, Galileo, GLONASS, GPS / QZSS, and more the device has internal storage for saving configurations.
Specifications:
- Part Number:51 single-chip microcomputer STM32 NEO7M
- RF Family/Standard:802.15.4
- Protocol: LoRa
- Modulation: FSK, GFSK, GMSK, MSK, OOK
- Frequency:137MHz - 525MHz
- Data Rate (Max):300kbps
- Sensitivity:-148dBm
NEO-7M GPS Pinout
This Module has 4 pins:
| Pin | Description |
|---|---|
| VIN | Module Power Supply (5V) - Provides power to the module. Typically requires a 5V power supply. |
| GND | Ground - Connect this pin to the ground reference of the system. |
| RX | Receive Data via Serial Protocol - Used to receive data from another device via a serial communication protocol, such as UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter). |
| TX | Transmit Data via Serial Protocol - Used to transmit data to another device via a serial communication protocol, such as UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter). |
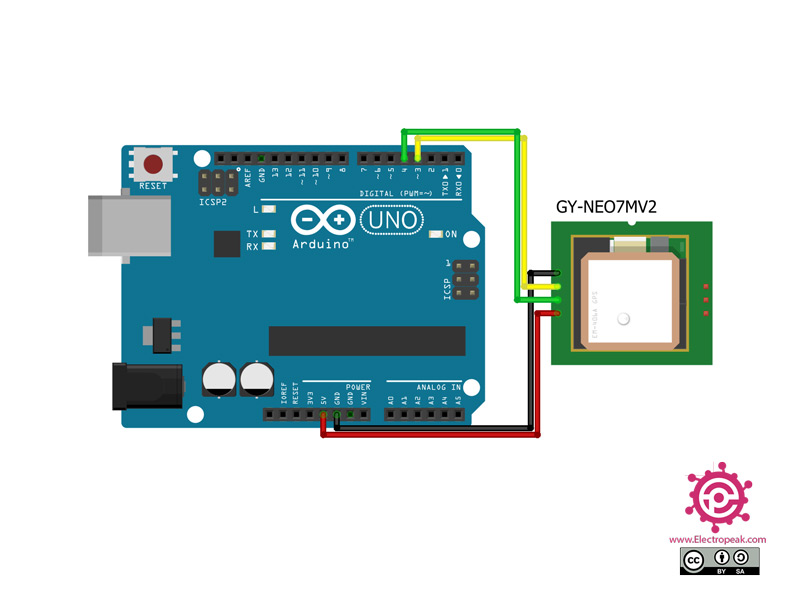
Connecting NEO-7M GPS With Arduino:
| NEO-7M GPSPin | Arduino Pin | Connection |
|---|---|---|
| Vin | VCC 5V | Power input (5V) |
| GND | GND | Ground |
| RX | Pin 4 | Input signal |
| TX | Pin 3 | Output signal |
- Download the library by clicking on the link provided: Download TinyGPSPlus Library.
- Open your Arduino IDE.
- Go to "Sketch" in the menu bar.
- Select "Include Library" > "Add .ZIP Library".
- Locate the downloaded .zip file of the TinyGPSPlus library on your computer.
- Select the .zip file and click "Open".
- The library will be added to your Arduino IDE.
Upload the Code:
#include "TinyGPS++.h"
#include "SoftwareSerial.h"
static const int RXPin = 4, TXPin = 3;
static const uint32_t GPSBaud = 9600;
TinyGPSPlus gps;
SoftwareSerial ss(RXPin, TXPin);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
ss.begin(GPSBaud);
Serial.println(F("DeviceExample.ino\nA simple demonstration of TinyGPS++ with an attached GPS module\nTesting TinyGPS++ library v. "));
Serial.println(TinyGPSPlus::libraryVersion());
Serial.println(F("by Mikal Hart\n"));
}
void loop() {
while (ss.available() > 0)
if (gps.encode(ss.read()))
displayInfo();
if (millis() > 5000 && gps.charsProcessed() < 10) {
Serial.println(F("No GPS detected: check wiring."));
while(true);
}
}
void displayInfo() {
Serial.print(F("Location: "));
if (gps.location.isValid()) {
Serial.print(gps.location.lat(), 6);
Serial.print(F(","));
Serial.print(gps.location.lng(), 6);
} else {
Serial.print(F("INVALID"));
}
Serial.print(F(" Date/Time: "));
if (gps.date.isValid()) {
Serial.print(gps.date.month());
Serial.print(F("/"));
Serial.print(gps.date.day());
Serial.print(F("/"));
Serial.print(gps.date.year());
} else {
Serial.print(F("INVALID"));
}
Serial.print(F(" "));
if (gps.time.isValid()) {
if (gps.time.hour() < 10) Serial.print(F("0"));
Serial.print(gps.time.hour());
Serial.print(F(":"));
if (gps.time.minute() < 10) Serial.print(F("0"));
Serial.print(gps.time.minute());
Serial.print(F(":"));
if (gps.time.second() < 10) Serial.print(F("0"));
Serial.print(gps.time.second());
Serial.print(F("."));
if (gps.time.centisecond() < 10) Serial.print(F("0"));
Serial.print(gps.time.centisecond());
} else {
Serial.print(F("INVALID"));
}
Serial.println();
}
After uploading the code, you can see the output in the serial monitor.