AED 68.25
Description
The GT-U7 module is a GPS receiver module renowned for its exceptional sensitivity, minimal power consumption, compact size, and superior tracking capabilities. It extends localization coverage even in challenging environments like urban canyons and dense jungles where standard GPS modules falter. This module boasts high precision positioning, low static drift, and effortless integration with 51 single-chip Arduino STM32 routines. Additionally, its USB interface allows seamless connectivity to a computer, eliminating the need for additional serial modules with IPX interfaces. Notably, it shares the NEO-6M chip with identical codes and pin configurations, simplifying integration for users.
Package Includes:
- 1 x GPS Module GT-U7 With NEO-6M
Features:
- High Sensitivity: The GT-U7 module is equipped with high sensitivity, making it exceptionally adept at receiving GPS signals even in challenging environments.
- Low Power Consumption: This module is designed for efficiency, consuming minimal power, and ensuring extended operation without draining your power source.
- Miniaturization: With its compact size and the option for straight or patch installation, it offers flexibility for different applications and installations.
- High Tracking Sensitivity: The GT-U7 module's high tracking sensitivity significantly expands its localization coverage, making it capable of precise positioning even in narrow urban skies or dense jungle environments where standard GPS modules may struggle.
- Compatibility with 51 Single-Chip Arduino STM32 Routines: It seamlessly integrates with 51 single-chip Arduino STM32 routines, simplifying the development process for various projects.
- USB Interface: Featuring a USB interface, this module allows direct connectivity to a computer using a mobile phone data cable, enabling real-time positioning data visualization on your computer screen.
- No Need for Additional Serial Modules: Unlike some GPS modules, the GT-U7 doesn't require additional serial modules with IPX interfaces. It can be directly connected to a computer via USB, functioning as a host computer serial port.
- Shared NEO-6M Chip: It employs the same NEO-6M chip, ensuring compatibility with existing codes and wiring, with minor adjustments for pin configurations.
Description:
The GT-U7 module stands out as a remarkable GPS receiver module that excels in sensitivity, efficiency, and versatility. Its high sensitivity allows it to capture GPS signals even in challenging environments such as narrow urban skylines and dense jungles, making it the preferred choice for high-precision positioning. What sets this module apart is not only its high tracking sensitivity but also its low power consumption, ensuring extended operational life without draining your power source. Its compact size and flexible installation options, either straight or patch, make it suitable for a variety of applications. it has a compatibility with 51 single-chip Arduino STM32 routines, simplifying the development process for a wide range of projects. Moreover, it comes equipped with a USB interface, allowing for direct connection to a computer using a mobile phone data cable. This feature enables real-time visualization of positioning data on your computer screen. Unlike some GPS modules that require additional serial modules with IPX interfaces, the GT-U7 module can be directly connected to a computer via USB, functioning as a host computer serial port. It shares the NEO-6M chip, ensuring compatibility with existing codes and wiring, with minor adjustments needed for pin configurations. this module offers a compact form factor measuring 27.6x26.6, with options for straight or patch installation and positioning holes for added convenience. It operates within a voltage range of 3.6V to 5V, making it adaptable to various power sources, including direct USB power supply. The default baud rate is set at 9600 but can be self-modified for customization. An IPEX antenna interface with a default active antenna ensures quick and accurate positioning.
Principle of Work:
Internal operation :
- GPS Antenna: The module has a built-in or external GPS antenna to receive signals from GPS satellites. These signals include precise timing information and data about the satellite's position.
- RF Front-End: The received GPS signals are passed through a radio-frequency (RF) front-end that amplifies and filters the signals. This step is crucial to enhance sensitivity and selectivity.
- Signal Processing: The module's internal processor then decodes the incoming GPS signals. It extracts information about the satellite constellation, including the position of each satellite and the time of signal transmission.
- Calculations: Using the information from multiple satellites, the module calculates its precise position on Earth through a process called trilateration. This involves determining the distance from the module to each satellite by measuring the time it takes for the signals to travel.
- Data Output: Once the position is calculated, the module can output this data in various formats, including the NMEA (National Marine Electronics Association) format, which is a common standard for GPS data.
Interaction with MCU (Microcontroller Unit):
- Serial Communication: The GT-U7 module typically communicates with the MCU through UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver-Transmitter) serial communication. It has two pins, TXD (Transmit Data) and RXD (Receive Data), that connect to the corresponding UART pins on the MCU.
- Baud Rate Configuration: The module operates at a default baud rate of 9600, but this can be modified if needed. The MCU needs to be configured to communicate at the same baud rate to ensure proper data exchange.
- Data Parsing: The MCU receives NMEA-formatted GPS data from the module. It needs to parse this data to extract relevant information, such as latitude, longitude, altitude, and time.
- Custom Coding: With the extracted GPS data, the MCU can execute custom code to perform various tasks. For example, it can display the location on an LCD screen, log the data to an SD card, or transmit it wirelessly.
- Integration with Other Sensors: The MCU can also integrate GPS data with other sensors or modules to create more complex applications. For instance, it can combine GPS data with temperature or humidity readings for environmental monitoring.
- Power Supply: The GT-U7 module typically operates within a voltage range of 3.6V to 5V. The MCU should provide a stable power supply within this range to ensure reliable operation.
Pinout of the Module:
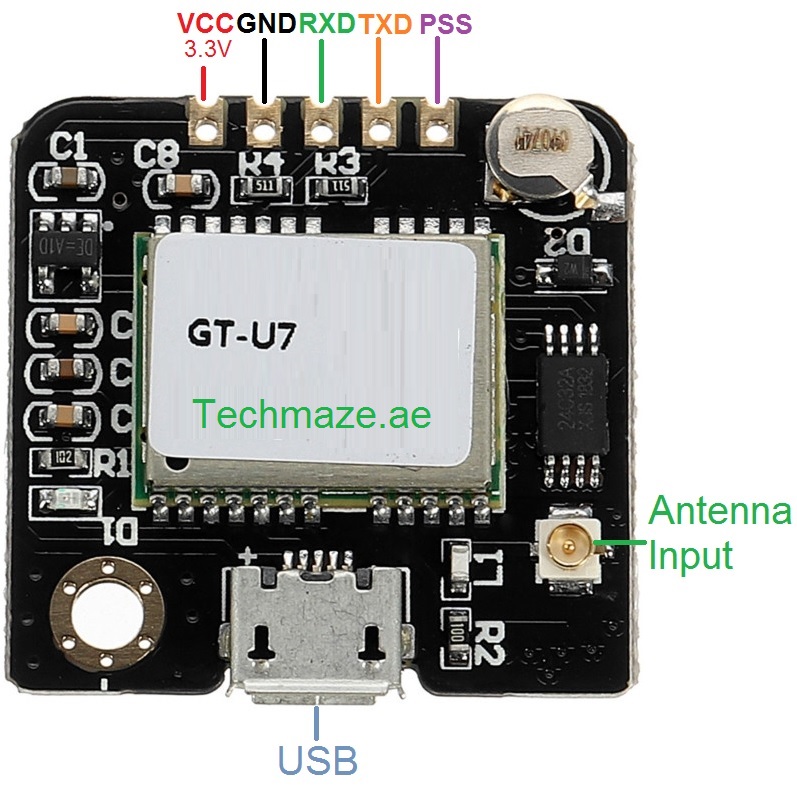
| Pin | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
| PPS | Pulse per second | PPS is a signal indicating one pulse per second. It's often used for precise timing and synchronization in applications like timekeeping. |
| TXD | Data Transmission Pin | TXD is the transmit data pin for serial communication. It is used to send data from the module to an external device, such as a microcontroller or computer. |
| RXD | Data Reception Pin | RXD is the receive data pin for serial communication. It is used to receive data from an external device, such as a microcontroller or GPS antenna. |
| GND | Ground | GND is the ground pin and serves as the reference point for the electrical circuit. It provides a common ground for all components in the system. |
| VCC | Power Voltage (3.6 to 5.5 Volts) | VCC is the power supply pin. It accepts a voltage input in the range of 3.6 to 5.5 volts to power the GT-U7 module. Make sure to provide a stable power source within this voltage range for reliable operation. |
Applications:
- Vehicle Tracking: The module is commonly used for real-time vehicle tracking and fleet management systems. It provides accurate location data, enabling businesses to monitor the movement of their vehicles for logistics, security, and optimization.
- Handheld Devices: GT-U7 can be integrated into handheld devices such as PDAs (Personal Digital Assistants) and smartphones to enable location-based services, navigation, and mapping applications.
- Vehicle Monitoring Systems: Beyond tracking, it is employed in-vehicle monitoring systems to gather data on vehicle performance, including speed, mileage, and route history.
- Mobile Phones: Mobile phones can benefit from the module for location-based features like geotagging of photos, check-in services, and navigation apps.
- Camcorders and Cameras: Cameras, including camcorders, can use the module for geotagging photos and videos, adding location information to media files.
- Shared Bikes and Scooters: The module can be used in shared bike and scooter systems to track the location of available vehicles and provide users with information on nearby options.
- Shared Mobile Power Devices: For shared mobile power banks or charging stations, the module can help in tracking their location, making it easier for users to locate and access them.
- Environmental Monitoring: Researchers and environmentalists use the module for fieldwork, allowing them to log precise GPS coordinates for environmental monitoring and data collection.
- Precision Agriculture: In agriculture, the module aids in precision farming, helping farmers optimize planting, irrigation, and harvest by providing accurate location data.
- Wildlife Tracking: Conservationists and researchers use GPS modules to track and study wildlife movements, helping to protect and conserve endangered species.
- Geocaching: Geocaching enthusiasts use GPS modules to locate hidden containers or "geocaches" in outdoor treasure-hunting games.
- Emergency Response: In emergency situations, the module can help first responders pinpoint the exact location of incidents, improving response times.
- Marine Navigation: While primarily a GPS module, it can also be used for marine navigation when combined with appropriate marine software and maps.
Circuit:

| GT-U7 Pin | Arduino Uno Pin |
|---|---|
| TXD | 2 (RX) |
| RXD | 3 (TX) |
| GND | GND |
| VCC | 5V |
Library:
The library used is already installed on Arduino IDE.
Code:
this code configures the Arduino to communicate with the GT-U7 GPS module via software serial, reads NMEA sentences from the module, and prints GPS data to the serial monitor. It specifically looks for "$GPGGA" sentences and displays them, which typically contain essential GPS information like latitude, longitude, altitude, and more:
#include "SoftwareSerial.h"
// Define the software serial object
SoftwareSerial gpsSerial(2, 3); // RX, TX (Connect GT-U7 RX to Arduino TX and GT-U7 TX to Arduino RX)
void setup() {
// Start the software serial communication
gpsSerial.begin(9600);
// Start the serial communication with the computer
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
if (gpsSerial.available()) {
char c = gpsSerial.read();
// Check if the character received is the start of a NMEA sentence
if (c == '$') {
String sentence = gpsSerial.readStringUntil('\n');
// Check if the sentence starts with "GPGGA" (GPS fix data)
if (sentence.startsWith("$GPGGA")) {
// Print the GPS data to the serial monitor
Serial.println(sentence);
}
}
}
}
- Library: The code begins by including the "SoftwareSerial" library, which is necessary for creating a software-based serial communication port on the Arduino Uno.
- Software Serial Configuration: The "gpsSerial" object is created using pins 2 and 3 to establish serial communication with the GT-U7 GPS module. It's important to connect the module's TX pin to Arduino's RX pin and module's RX pin to Arduino's TX pin as specified in the comments.
- Setup Function: In the "setup()" function, two serial communication channels are initialized:
- "gpsSerial" is configured for communication with the GPS module at a baud rate of 9600, matching the module's baud rate.
- "Serial" is initialized for communication with the computer at the same baud rate (9600) for displaying GPS data in the Arduino IDE's serial monitor.
-
Loop Function: The "loop()" function continuously performs the following tasks:
- It checks if there is data available on the "gpsSerial" software serial port.
- If data is available, it reads a character and stores it in the variable "c."
- It checks if the received character is a dollar sign ('$'), indicating the start of a new NMEA sentence.
- If a new sentence is detected, it reads the entire sentence until a newline character ('\n') is found and stores it in the "sentence" variable.
- It checks if the "sentence" starts with "$GPGGA," a specific NMEA sentence containing GPS fix data.
- If the sentence is a "$GPGGA" sentence, it prints the entire sentence to the serial monitor using "Serial.println(sentence)."
Technical Details:
- Size: 27.6x26.6 mm
- Working Voltage: 3.6V-5V (or direct USB power supply)
- Work Baud Rate: 9600 (self-modification)
- Antenna Interface: IPEX (Default distribution of active antenna)
- Onboard Rechargeable Button Cell
- Onboard E2PROM for parameter data storage
- NEMA Output Format Compatibility with NEO-6M
Resources:
Comparisons:
While the GT-U7 module offers some distinct features like high sensitivity, miniaturization, and a built-in USB interface, it shares the NEO-6M chip and maintains compatibility with NMEA output formats:
Differences:
- Sensitivity and Tracking: The GT-U7 module is advertised as having high sensitivity and high tracking sensitivity, which may result in better performance in challenging GPS signal environments. NEO-6M modules also offer good sensitivity but may not match the claimed high sensitivity of the GT-U7.
- Miniaturization: The GT-U7 module is compact, measuring 27.6x26.6 mm. This indicates a smaller form factor compared to some NEO-6M modules, which can vary in size depending on the manufacturer and model.
- USB Interface: The GT-U7 module features a USB interface, allowing direct connection to a computer using a mobile phone data cable. In contrast, traditional NEO-6M modules typically communicate with an MCU via UART and may require additional hardware for USB connectivity.
- E2PROM for Parameter Data: GT-U7 has onboard E2PROM, which enables users to save parameter data. NEO-6M modules may or may not have this feature, depending on the specific model.
Similarities:
- Chip Compatibility: Both the GT-U7 module and NEO-6M modules use the same NEO-6M chip. This means that the core GPS functionality and data format compatibility are likely to be similar.
- Working Voltage: Both modules typically operate within a similar working voltage range of 3.6V to 5V, providing flexibility in power supply options.
- Baud Rate: Both modules can be configured to work at a specific baud rate. The default baud rate for many GPS modules, including NEO-6M, is often set to 9600, which is a common standard for GPS communication.
- NMEA Output Format: Both modules typically provide GPS data in NMEA (National Marine Electronics Association) format, making them compatible with various software and applications that can parse NMEA sentences.